It’s a common question, especially for those delving into computer specifications: How much RAM is DDR4 ?” The answer, surprisingly, is that DDR4 RAM isn’t a specific amount of memory itself; rather, it refers to a type or generation of Random Access Memory .
Think of it like asking, “How much capacity is a solid-state drive (SSD)?” An SSD isn’t a single, fixed capacity; it’s a form of storage technology that comes in various sizes (e.g., 250GB, 500GB, 1TB). Similarly, DDR4 is a technology standard, and individual modules (often called “sticks”) are manufactured in different capacities.
What Does DDR4 Actually Mean?
DDR4 stands for “Double Data Rate Fourth Generation.” It’s the successor to DDR3 and precedes the newer DDR5 standard. Each generation of DDR RAM brings improvements in performance, power efficiency, and capacity.
Introduced around 2014, it rapidly became the industry standard for most consumer and enterprise computers by the mid-2010s. If you bought a new laptop or built a desktop PC in Kenya anytime from roughly 2016 to late 2021/early 2022, chances are it came equipped with it.
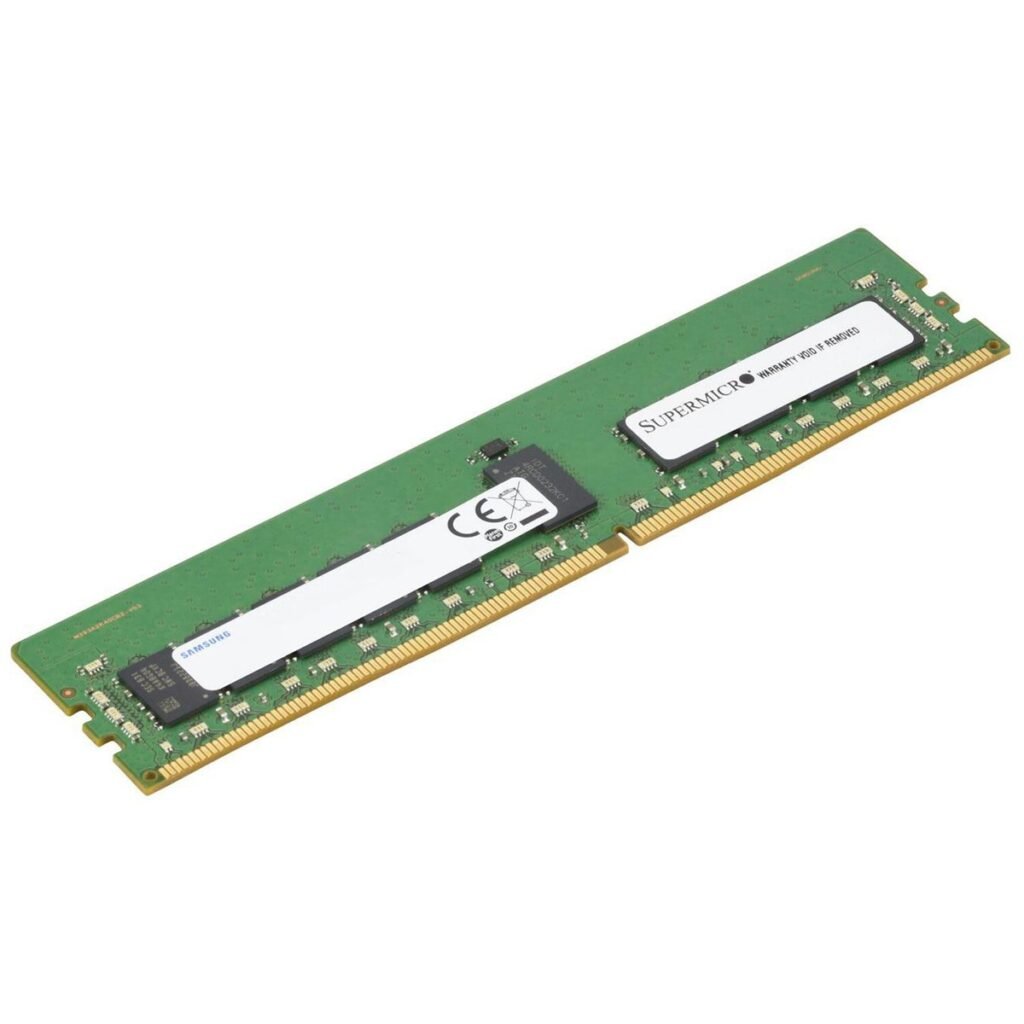

Key Characteristics and Benefits of DDR4 RAM
Compared to its predecessor, DDR3, DDR4 offers several significant advantages:
- Higher Speeds (Measured in MHz):
- It’s modules typically start at speeds of 2133 MHz (Megahertz) and commonly go up to 3200 MHz. High-performance or overclocked DDR4 RAM can reach speeds of 3600 MHz, 4000 MHz, or even higher.
- Faster RAM speeds allow the CPU to access data quicker, leading to overall snappier system performance, faster application loading, and smoother multitasking.
- Lower Power Consumption (Measured in Volts):
- It operates at a lower voltage, typically 1.2V, compared to DDR3’s 1.5V or 1.35V (for DDR3L).
- This reduced voltage makes DDR4 more energy-efficient, which is particularly beneficial for laptops as it contributes to longer battery life and less heat generation.
- Increased Module Density and Capacity:
- DDR4 technology allows for the creation of individual RAM modules with higher storage capacities.
- While DDR3 modules often topped out at 8GB or 16GB per stick for common consumer use, DDR4 commonly sees individual sticks of 4GB, 8GB, 16GB, and 32GB. This enables systems to achieve much higher total RAM amounts (e.g., 64GB or even 128GB in systems with multiple slots).
- Physical Differences (Compatibility):
- DDR4 RAM modules have a different pin count and notch placement compared to DDR3.
- Desktop DDR4 (DIMM): Has 288 pins.
- Laptop DDR4 (SODIMM): Has 260 pins.
- This physical difference means you cannot install a DDR4 module into a DDR3 slot, or vice-versa. Attempting to force it can damage both the RAM and the motherboard.
So, “How Much RAM” is Actually DDR4 RAM?
To reiterate, DDR4 is the type of RAM. When someone talks about the “amount” of RAM, they’re referring to the total capacity of the DDR4 modules installed in a system.
For example:
- A laptop might have 8GB DDR4 (which could be one 8GB stick or two 4GB sticks).
- A gaming desktop might boast 32GB RAM (perhaps two 16GB sticks or four 8GB sticks).
- Even an entry-level machine might have 4GB DDR4 RAM (typically one 4GB stick).
The choice of how much RAM a system has is made by the manufacturer (or by the user if they’re building or upgrading).
Why is DDR4 Still Relevant in Kenya (and Globally)?
While DDR5 is the latest and fastest RAM standard, DDR4 remains highly relevant, especially in markets like Kenya for several reasons:
- Cost-Effectiveness: DDR4 RAM and DDR4-compatible motherboards/CPUs are generally more affordable than their DDR5 counterparts. This makes DDR4 systems excellent value for money.
- Widespread Availability: It is is mature technology, meaning modules are readily available from numerous brands in various capacities and speeds across most tech shops in Nairobi and beyond.
- Performance for Most Users: For the vast majority of users – students, professionals, casual gamers, and everyday multi-taskers – offers more than enough speed and capacity to handle their computing needs smoothly.
- Upgrade Path for Existing Systems: If you have a DDR4-compatible laptop or desktop with 4GB or 8GB RAM, upgrading to 16GB or 32GB of DDR4 is a straightforward, cost-effective, and highly impactful way to boost performance without needing a whole new system.
| Memory Type | Capacity | Speed (Frequency) | Price (KES) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DDR2 | 2 GB | 5300U | 1,000 |
| DDR2 | 2 GB | 6400U | 1,000 |
| DDR3 | 4 GB | 10600U | 1,500 |
| DDR3L | 4 GB | 12800U | 1,500 |
| DDR3L | 8 GB | 12800U | 3,500 |
| DDR4 | 4 GB | 2133 | 1,700 |
| DDR4 | 4 GB | 2400 | 1,700 |
| DDR4 | 4 GB | 2666 | 1,700 |
| DDR4 | 4 GB | 3200 | 2,000 |
| DDR4 | 8 GB | 2133 | 4,000 |
| DDR4 | 8 GB | 2400 | 4,000 |
| DDR4 | 8 GB | 2666 | 4,000 |
| DDR4 | 8 GB | 3200 | 4,000 |
| DDR4 | 16 GB | 2400 | 6,000 |
| DDR4 | 16 GB | 2666 | 6,000 |
| DDR4 | 16 GB | 3200 | 6,500 |
| DDR4 | 32 GB | 2666 | 13,000 |
| DDR4 | 32 GB | 3200 | 14,000 |
| DDR4 | 64 GB | 2666 | Out of Stock |
| DDR4 | 64 GB | 3200 | Out of Stock |
In conclusion, when you hear “DDR4,” remember it refers to the advanced technology of the memory modules themselves, designed to provide faster, more efficient performance than previous generations. The “how much” aspect comes down to the individual capacity (e.g., 4GB, 8GB, 16GB) of the DDR4 sticks installed in your system. Understanding this distinction is key to making informed decisions about your computer’s memory.































 ASUS
ASUS